
In August 2022, China Insurance Security Fund Co., Ltd. released the Risk Assessment Report of the Chinese Insurance Industry 2022 (hereinafter referred to as the “Report”) in Beijing. The Report observes that in 2021 the insurance industry adhered to the people-centric development philosophy as always and firmly followed the high-quality development path; the insurance industry maintained stable operation, the security function of insurance was further strengthened, and the quality and efficiency of the services for the real economy improved; the reforms in key areas were deepened, significant achievements were made in forestalling and defusing financial risks, and the role of the insurance industry as the “stabilizer” of the society and the “booster” of the economy was effectively played. Impacted by the pandemic, the domestic situation was changing faster and the external environment was more complex and severe, further increasing uncertainty. The Chinese insurance industry is faced with many difficulties and challenges, and risks in some key areas must be paid attention to.
The Report consists of four parts, namely, the economic and financial environment, the state of the industry, the risk assessment of the industry, and experts’ observations. On the basis of the review of the internal and external environments of the insurance industry in 2021, the Report provides a comprehensive description of the trends of the industry and an analysis of the current risks and problems in the insurance industry.
I. State of Operation
In 2021, the insurance industry was stable on the whole. The asset scale grew steadily. The total assets of insurance companies were RMB24.9 trillion, an increase of 11.5% from the beginning of the year. The scale of the insurance business recorded positive growth. The original insurance premium income posted RMB4.49 trillion, a year-on-year increase of 4.05%. The solvency maintained within a reasonable range. The average comprehensive solvency margin ratio of the 179 insurance companies included into the review by the Solvency Regulatory Committee was 232.1%.
The capability of the insurance industry in serving economic and social development improved significantly. The insurance industry participated in the continuous innovation in the social security system, the scale of the health insurance business continued to expand, and urban inclusive insurance was flourishing. The services for the development of the real economy were intensified. As of the end of November in 2021, insurance funds provided RMB20.4 trillion financing to the real economy in various forms. Remarkable results were achieved in serving the rural revitalization strategy. In 2021, agricultural insurance provided RMB4.72 trillion risk coverage to 178 million farmer accounts.
In terms of property insurance, the sector continued to promote the supply-side reform. The premium increased slightly. Throughout 2021, the sector realized RMB1.3676 trillion original premium income, a year-on-year increase of 1.92%. The insurance type structure was further optimized, with the proportion of non-auto insurance premium rising for the sixth year straight. The security function was strengthened. The insured amount increased by 45.53% year on year. The operating results improved. Both net operating cash inflows and net profit rose slightly year on year. The solvency margin ratio also increased slightly year on year.
In terms of life insurance, the sector actively explored transformation. The original insurance premium income went up a little and security businesses such as health insurance maintained stable development. In terms of channels, the agent channel shrank while the bancassurance channel sustained growth. As it was seeking a high-quality development path, the sector, which puts the people’s livelihood in the first place, saw its service capability further strengthened. Even though the total net profit of the sector decreased, its solvency stayed within a reasonable range.
In terms of fund utilization, the amount of insurance funds utilized maintained stable growth, the asset allocation ratios were basically stable, while the rate of return on fund utilization decreased year on year. The overall investment capacity coverage of the sector expanded and the equity investment capability of insurance institutions improved significantly. The insurance funds used to provide financing for the real economy increased substantially, with many being used to support major national strategic projects and key areas.
II. Risk Assessment
In 2021, the insurance industry adhered to the people-centric development philosophy and firmly followed the high-quality development path. The industry maintained stable operation, the security function was strengthened, and the quality and efficiency of the services for the real economy improved. Meanwhile, impacted by the pandemic, the domestic situation was changing faster and the external environment became even more complex and severe, further increasing uncertainty. The insurance industry was faced with many difficulties and challenges.
The Report seeks to summarize the new trends of the risks of the industry, give a systematic analysis of the main risk points in key areas and critical procedures, continue to pay attention to traditional risks and problems, and attach great importance to emerging risk exposure. The Report has summarized the six main risks and challenges faced by the Chinese insurance industry over the past year and at present as follows:
In terms of strategy risk, most of the small and medium-sized companies in the property insurance sector cannot determine the direction of strategic transformation and have difficulties in the operation of auto insurance and non-auto insurance businesses, and over half of them have recorded underwriting losses for five years straight. In terms of auto insurance, most small and medium-sized companies lack quality control capability and are unable to dilute fixed cost. As a result, their combined ratio and combined expense ratio are higher than those of large companies and they have suffered great underwriting losses. In terms of non-auto insurance, some small and medium-sized companies lack strategic focuses in development or a long-term plan for their operation. They are seeking immediate premium growth and have ignored the long-tail risk of the non-auto insurance business. The life insurance sector is faced with transformation challenges. Due to the Covid-19 pandemic, problems that have accumulated from the past extensive operation mode have emerged at a faster speed. How to achieve high-quality development has become the topic of the year 2021. At present, the life insurance sector is at the critical period of transformation and new businesses are under development pressure. In terms of channels, the industry is faced with challenges like shrinkage of the agent channel and stricter regulatory requirements for the internet channel. In terms of product, in addition to the challenges of weak critical illness insurance sales and changes in the product term structure, how to improve the operation quality and efficiency of products like Medicare, whole life insurance and old-age insurance has also become the research subject of the industry.
In terms of credit risk and market risk, first, credit risk has increased. Default is still a serious problem in the credit market. The credit risk faced by insurance companies has risen, and the rate of rise of credit risk is much higher than that of the growth rate of assets. At insurance companies, credit risk has led to increase in potential losses, so their provisions for asset impairment have increased substantially. In future, the pressure of credit risk is expected to continue to increase and to set aside provisions for asset impairment for credit events is likely to become a routine of insurance companies. Second, the equity market has become more volatile and equity investments vary greatly. Some companies concentrate too many of their investments in certain industries or individual stocks, which can have an adverse impact on return on investment. Third, spread loss risk has increased. In the environment that interest rates have been falling for a long time, the return on investment of the insurance industry which mainly invest in fixed-income targets is expected to fall. Mature assets and new assets cannot sustain original return. However, as the cost of debt is relatively rigid, interest spreads will gradually shrink, so reinvestment risk and spread loss risk are high.
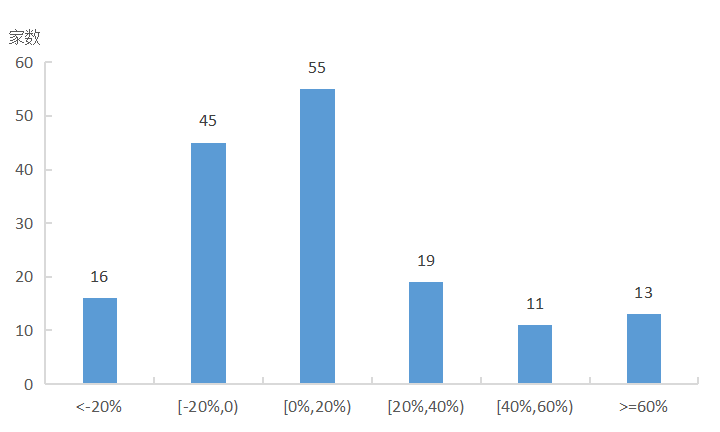
Source: Abstract of the report on the solvency of insurance companies in 2020 and 2021
Figure 1 Increase of minimum capital of credit risk at the end of 2021 from the beginning of the year
In terms of insurance risk, first, the loss ratio of liability insurance is under great upward pressure. The main reasons are: as competition intensifies, rates are low and premium adequacy decreases; personal injury compensation has increased year by year, which has driven up the business claim cost; the legal risk exposure faced by relevant occupations involving the financial field such as listed companies’ directors, supervisors and senior management has clearly increased; ex-ante prevention service capability, risk identification capability and risk control capability are weak. Second, compensation relating to natural disasters has increased. In 2021, China had many extreme weather and climate events, with distinctive phase and regional characteristics. The frequent catastrophe risk events resulted in increase in casualties and property losses, thus the insurance industry’s compensation expenses grew rapidly. Third, the critical illness insurance business is under pressure. On the one hand, affected by customers making overdrafts in advance, insufficient effective consumer demand, bottlenecks encountered by channels, short product supply and the crowding-out effect of short-term health insurance products, the sales of the critical illness insurance products under the new definition fell short of expectations. On the other hand, the incidence rate and detection rate of critical illnesses are on a rising trend. Meanwhile, the preferred claims policy and the multiple claims clause have, to some extent, increased compensation. In addition to life insurance companies’ lack of capabilities in claim verification and risk identification, the compensation for critical illness compensation has increased rapidly.
In terms of corporate governance risk, insurance companies need to improve their governance effectiveness. Changes in the equity structure, a high ratio of pledged equity, frequent changes in or long-term vacancy of senior management members, etc. can affect the continuity and effectiveness of companies’ long-term strategies and thus directly affect companies’ stable operation and long-term development. According to the statistics of the information disclosed by 167 insurance companies, a total of 28 insurance companies had equity changes in 2021, of which, eight changed their equity structures twice in the year. As at the end of 2021, about one fifth of insurance companies had pledged or frozen shareholder equity, of which, four had over 50% pledged or frozen equity. Moreover, a few companies had complex shareholder relationships, and share-holding entrustment and implicit shareholders were the most prominent problems. Some companies had held illegal equity that needs to be dealt with for a long time. The unstable equity structure directly led to frequent changes in and long-term vacancy of senior management. Among the companies that had changes in their equity structures in 2021, ten also saw changes in chairman or general manager and seven didn’t have a chairman or a general manager.
In terms of capital inadequacy risk, the capital supply-demand mismatch in the insurance industry can increase the capital pressure of insurance companies, especially small and medium-sized insurance companies. On the demand side, the capital demand of the insurance industry has continuously increased, which is mainly due to the long operation and earnings cycle of the insurance industry and the poor profitability of most small and medium-sized insurance companies. Among the 145 small and medium-sized property insurance companies and small and medium-sized life insurance companies that disclosed their 2021 financial reports, 90 recorded negative undistributed profit. They were unable to accumulate profit from their operations and transfer it to their paid-in capital. On the supply side, social capital is less willing to enter the insurance industry, leading to decrease in supply of external capital. In 2021, the amount of bonds issued for capital increase decreased and the fever of non-listed insurance company licenses went down. The main reasons include: first, as most small and medium-sized insurance companies are unable to provide long-term, stable returns on capital, existing shareholders lack the willingness to increase capital and potential investors are not attracted. Second, with insurance regulators issuing stricter requirements on corporate governance, social capital has become more rational and no longer enters the insurance industry blindly. There are only a few willing, substantial investors that meet qualification requirements. Third, the general economic environment is under pressure. The existing shareholders of some insurance companies are under great pressure in operation and both their capability and willingness to increase capital have decreased.
In terms of operational risk, the concept of compliant operation needs to be stressed. Specifically, first, charges and commissions payment in violation of regulations is a serious problem. Some companies use high fee incentives to grab market shares, obtain funds by listing false operating expenses, false intermediate services, false marketing labor, etc., use them to pay excess charges or give other interests than those specified in the insurance policy to the policy holder, encourage branches to conduct illegal business in order to reach KPIs, and disrupt the market order. Second, sales misleading is still the main reason that life insurance companies receive administrative penalties and consumer complaints. In 2021, among the complaints about life insurance companies received by regulators, sales disputes and complaints accounted for 43.62%. Third, small and medium-sized companies and primary-level branches lack compliance management. The penalty amounts of some small and medium-sized insurance companies are higher than their market shares, and the tier-three and tier-four primary-level branches of insurance companies have received more punishment. The primary-level branches of insurance companies lack compliance awareness, and don’t have adequate input in compliance building, and cannot effectively implement internal control policies and regulations.
III. Experts’ Observations
The experts of the risk assessment expert committee of the insurance industry have written seven articles about risk observations for the Report, which have reflected the experts’ research results on the industry segments.
In terms of property insurance business, regarding new energy vehicle (NEV) insurance, experts believe that supported by national industry policies, the auto industry has accelerated transformation and the development of NEVs is unstoppable. However, because the expected compensation risk of NEV insurance is much higher than that of traditional fuel vehicle insurance, property insurance companies are not very enthusiastic about NEV insurance. On the industry level, the exclusive NEV insurance products have reduced the average cost per policy, raising higher requirements on the operation of NEV insurance. In addition, emerging new auto models and new technologies, the application of UBI and intelligent driving data and innovative additional terms have put insurance companies under great pricing risk. Experts have given two suggestions, first, to mobilize the whole industry to promote the reform of the industrial chain so as to effectively increase the insurance industry’s negotiation power with the auto industry and second, to accumulate data to improve pricing analysis and claims management capabilities. Regarding agricultural insurance, experts think that the complex nature of the target of agricultural insurance is the root cause of the difficulty in operating the business. For various reasons, a single insurance company has difficulties in pricing agricultural insurance products independently and has to rely on the industry and relevant government departments to complete the pricing. At present, the third line of defense for catastrophe risk dispersion in agricultural insurance cannot achieved its function as expected. Moreover, regarding crop insurance, experts advise insurance applicants to select different security levels to achieve better effect, as the government provides different subsidiary proportions for different security levels.
In terms of life insurance, experts believe that the bancassurance channel faces both opportunities and challenges. According to the new asset management rules, products like banks’ wealth management products cannot pledge products with principal and interest guaranteed or with rigid redemption, so insurance products, which are defined-benefit products, become more attractive to customers. However, the industry still needs to actively explore ways to realize value conversion of the bancassurance channel and change product homogeneity and vicious fees competition in the industry. Meanwhile, experts say that the bancassurance channel shall not only solve the problems about scale and value but also reshape the business model using the three factors of outlets, customers and products. Experts have given three suggestions, first, to segment products and stress the unique advantages of insurance; second, to control cost and build core profitability; and third, to prevent sales misleading and realize high-quality development of the bancassurance channel. Regarding health insurance business, experts believe that inclusive commercial health insurance is a strong tool to alleviate residents’ medical expense burden and bolster the multi-tiered medical security system, but it is faced with the following risks and challenges in the course of rapid development. It can easily cause adverse selection. After multiphase operation, it will be probably affected by the “death spiral” effect. Participation and renewal of insurance are unsatisfactory. Operators cannot establish reliable and effective communication and decision-making, thus affecting operation efficiency, and the operation mechanism needs to be optimized. Marketing and publicity are not standardized. To solve the foregoing problems, experts suggest adhering to compliance, avoiding following suit, and promoting targeted product development. Moreover, experts suggest exploring diversified fundraising modes, strengthening the guidance of government departments and associations on the operation throughout the whole process, and establishing information disclosure regulations. Regarding old-age insurance business, experts think that old-age insurance products and services are currently short supply with increasing elderly demand, and even though the third pillar industry individual old-age insurance and savings have great development potential, it is spontaneous and scattered. When solving the problem of insufficient sources and reserve on the income end, experts say we should explore new product and service forms on the elderly care expense and consumption end. Experts suggest setting a clear positioning, giving play to the advantages of insurance, and developing products with customers at the center on the income end; and paying equal attention to the development of high-end and home-based care for the aged on the expense and consumption end.
In terms of asset management, experts believe that in view of the new impact of the rules of Phase II of the Solvency Regulations of Insurance Companies II on the allocation of insurance assets, regarding insurance funds, we should adjust the underlying logic of the allocation of insurance assets from the perspective of capital constraint; on the management level, we should improve investment management capability and adapt to the new situation and new requirements as quickly as possible; in terms of investment variety, we should refine investment management and search for investment varieties with low capital consumption; and on the product level, we should seek new solutions for optimization of solvency. Experts suggest that insurance asset management companies shall assist insurance funds finding products with better investment cost performance; take into full account the impact of capital consumption and develop standardized, penetrative portfolio products with a simple hierarchy; optimize the system building according to regulatory rules to provide timely and effective penetrating measurement data support to clients. Experts believe that in the complex environment, small and medium-sized insurance asset management companies need to follow the high-quality development path. Currently, compared to super-large companies and large companies, small and medium-sized insurance asset management companies are under even greater survival pressure and they find it even more difficult to balance risk prevention and development. To ensure high-quality development and effective risk control, small and medium-sized insurance asset management companies need to attach importance to strategy planning and maintain strategic focuses, adhere to the business philosophy of opening up, cooperation and win-win results, put forth effort to strengthen capability building, and strive to improve risk control capability.

